Optimal Timing for Foundation Repairs
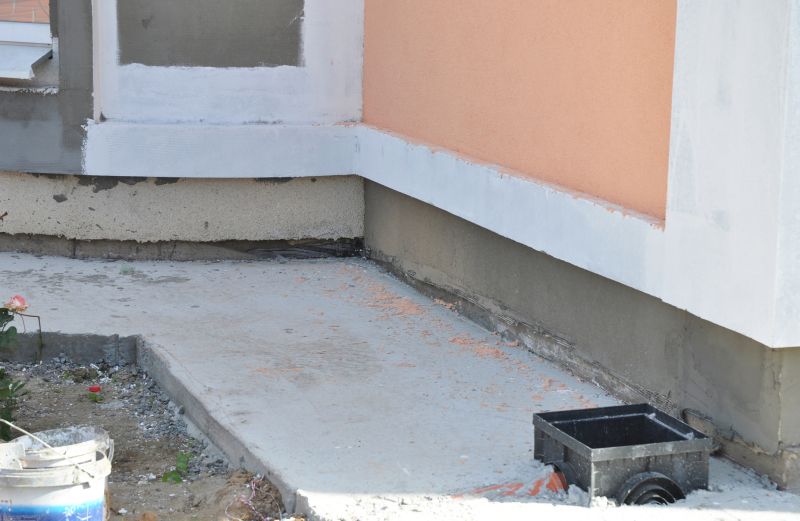

Ways to make Foundation Repairs work in tight or awkward layouts.
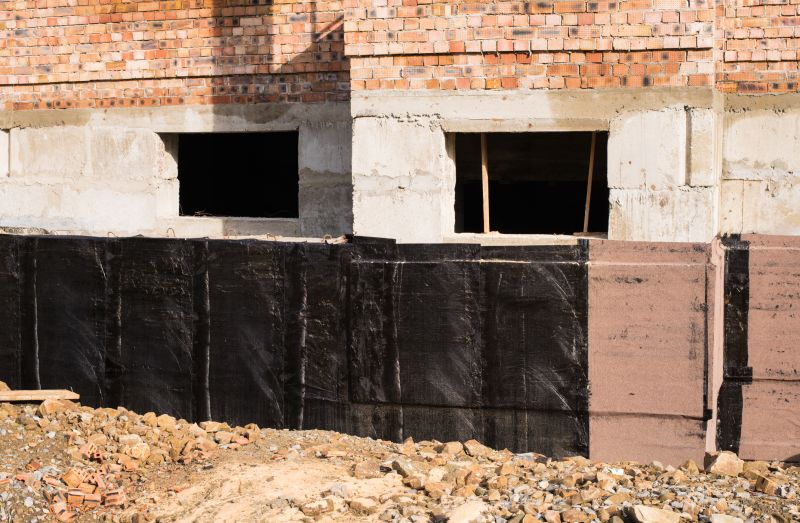

Popular materials for Foundation Repairs and why they hold up over time.
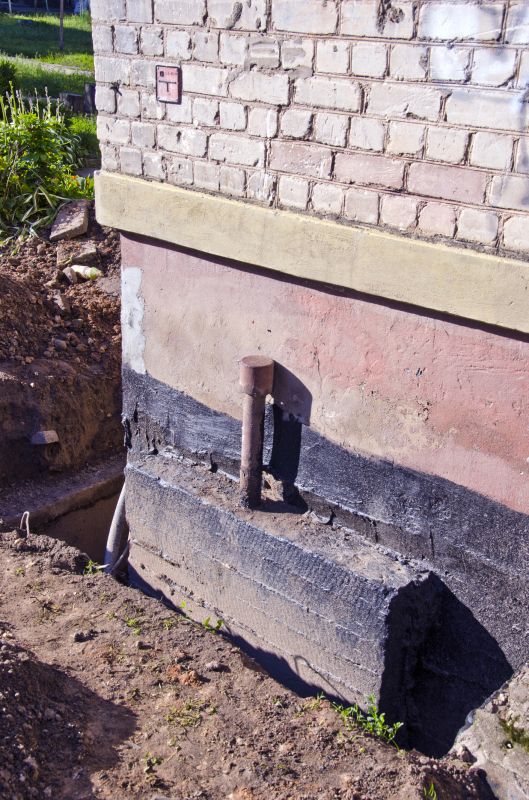

Simple add-ons that improve Foundation Repairs without blowing the budget.
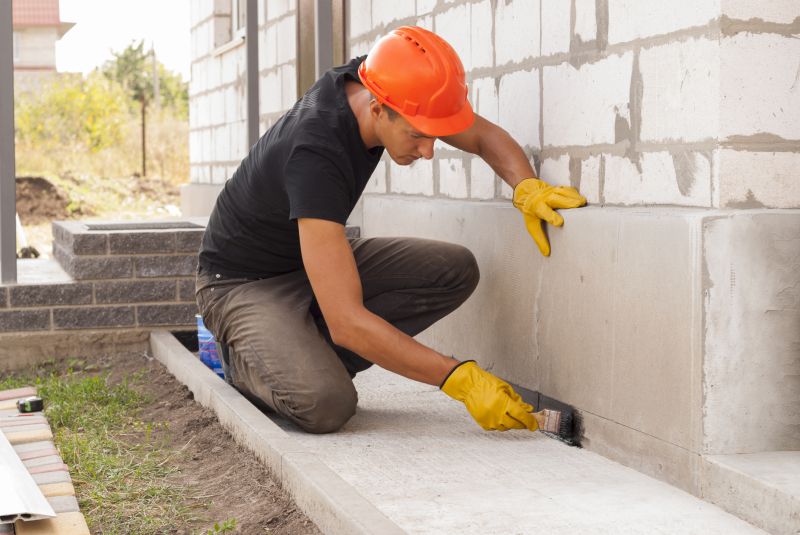

High-end options that actually feel worth it for Foundation Repairs.
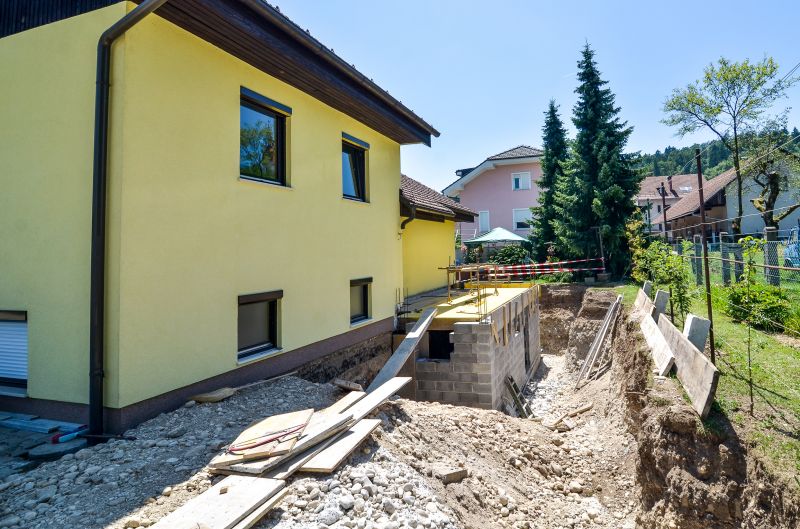

Finishes and colors that play nicely with Foundation Repairs.
Little measurements that prevent headaches on Foundation Repairs day.
Foundation repairs are essential for maintaining structural integrity and preventing further damage to a property. The timing of repairs can influence the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of the work. Typically, the best time for foundation repairs depends on weather conditions, soil moisture levels, and the severity of the damage. Repairing during periods of stable weather helps ensure that materials cure properly and that the soil remains stable, reducing the risk of new issues arising.
In regions with significant seasonal changes, such as Minnesota, it is often recommended to schedule foundation repairs during late spring or early fall. These periods usually offer moderate temperatures and soil conditions that are less prone to shifting. Cold winter months or the hot, dry summer can pose challenges, such as frozen ground or excessive soil shrinkage, which may complicate repair work. Proper timing can lead to longer-lasting results and minimize disruptions.
Spring offers moderate weather and soil conditions ideal for foundation work. It allows repairs to settle before the summer heat or winter freeze.
Summer can be challenging due to high temperatures and dry soil, but repairs are possible with proper planning.
Fall provides cooler temperatures and moist soil, which can be beneficial for foundation stabilization and repair.
Winter is generally less suitable due to frozen ground, which can hinder excavation and curing processes.
| Season/Condition | Suitability for Foundation Repairs |
|---|---|
| Spring | Ideal, moderate weather and soil conditions |
| Summer | Possible with precautions due to heat and dryness |
| Fall | Optimal, cooler temperatures and moist soil |
| Winter | Generally not recommended due to frozen ground |
| Dry seasons | Challenging due to soil shrinkage |
| Wet seasons | Possible but requires extra precautions |
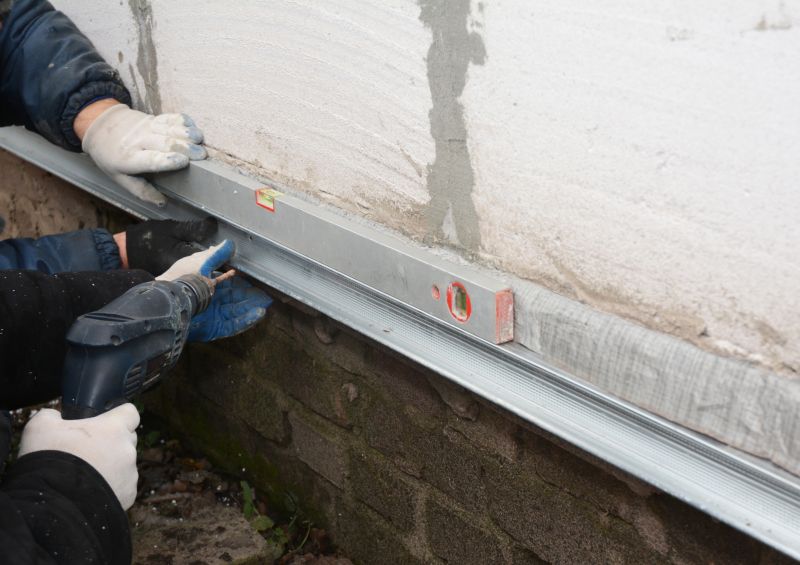

A 60-second routine that keeps Foundation Repairs looking new.
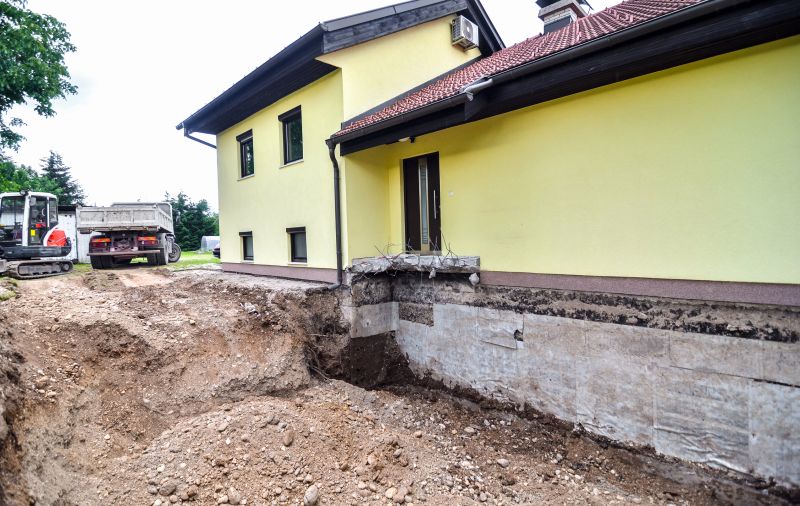

A frequent mistake in Foundation Repairs and how to dodge it.
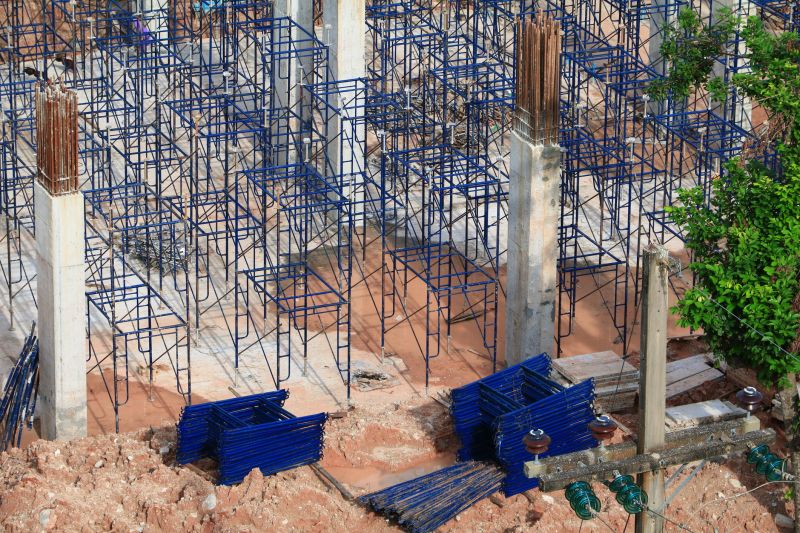

Small tweaks to make Foundation Repairs safer and easier to use.
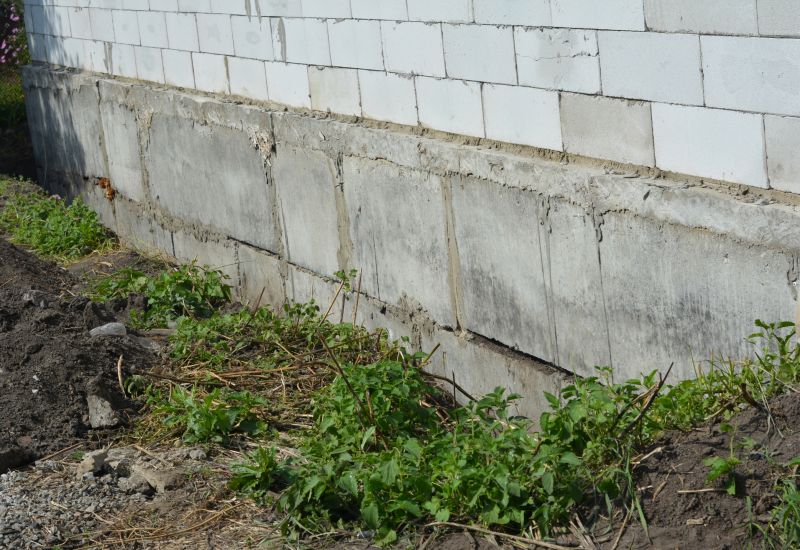

Lower-waste or water-saving choices for Foundation Repairs.
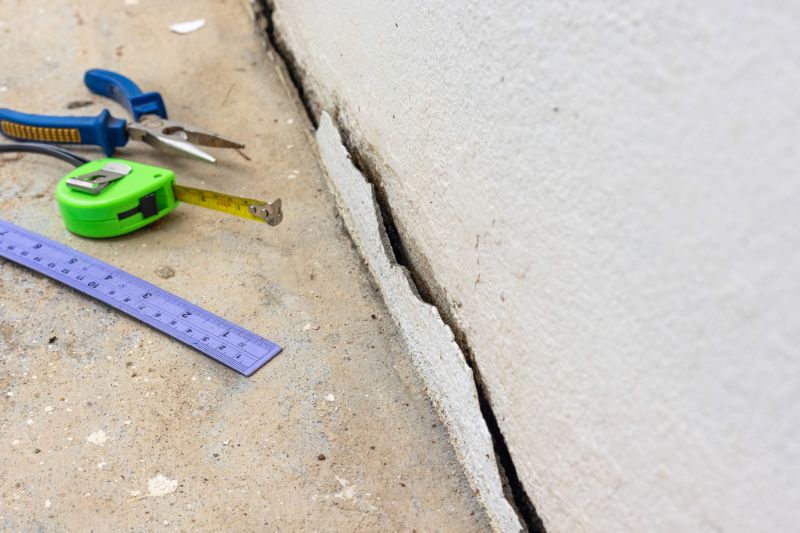

The short, realistic tool list for quality Foundation Repairs.

Rough timing from prep to clean-up for Foundation Repairs.
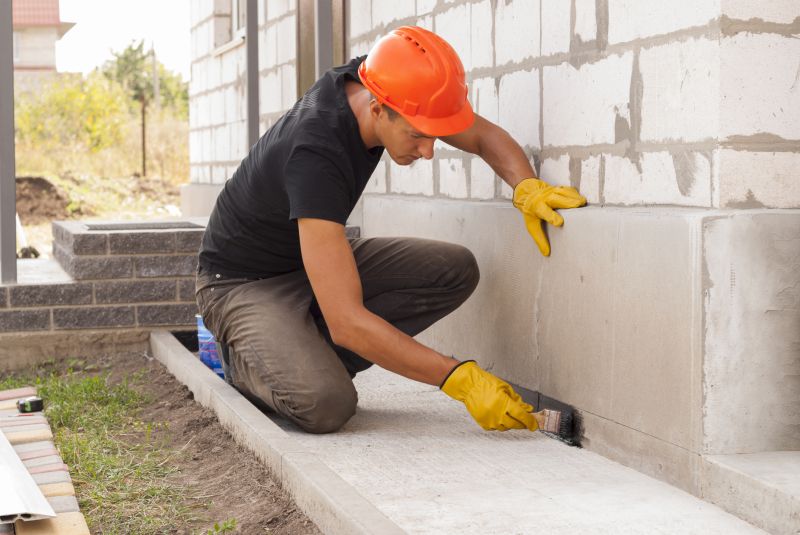

Quick checks and paperwork to keep after Foundation Repairs.
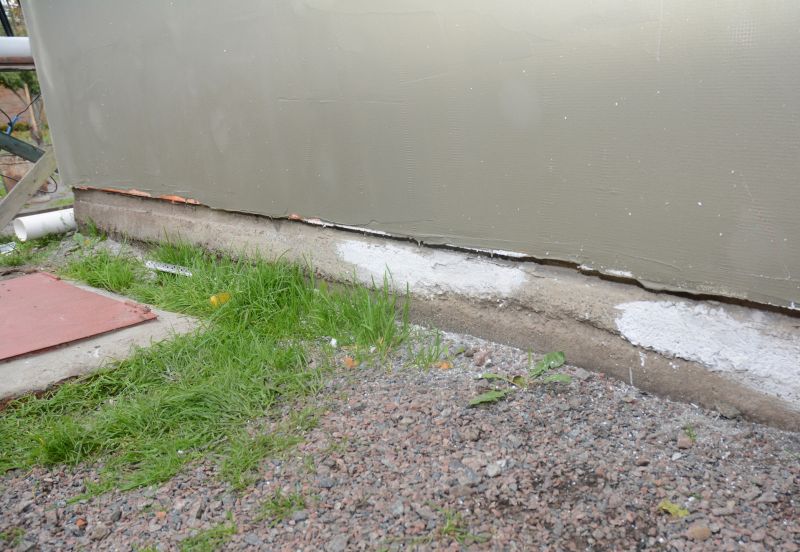

Examples that show the impact a good Foundation Repairs can make.
Foundation repairs are crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of a structure. The process often involves assessing the extent of damage, soil analysis, and selecting appropriate repair methods such as underpinning, piering, or crack injection. Proper timing ensures that repairs are effective and durable, reducing the risk of future issues caused by soil movement, water intrusion, or structural stress. Regular inspections and timely repairs can extend the lifespan of a foundation significantly.
Understanding the optimal timing for foundation repairs requires consideration of local climate patterns and soil conditions. In Minnesota, seasonal variations can influence soil moisture levels, which directly affect foundation stability. Repair work performed during periods of soil stability minimizes the chance of reoccurring problems. Consulting with foundation specialists can help determine the best window for repairs based on specific site conditions.
Timely repairs prevent further structural damage, reduce long-term costs, and improve property value.
Cracks in walls, uneven floors, and sticking doors are common indicators of foundation issues.
Methods include underpinning, slab jacking, and crack injection, tailored to specific damage types.
Soil type and moisture levels significantly influence foundation stability and repair strategies.



